If you’ve ever searched “ETF meaning” or heard about the Bitcoin ETF buzz and wondered what it’s all about, you’re not alone. ETFs, short for Exchange-Traded Funds, have quietly become one of the most powerful tools in global finance. They’re simple to trade, easy to understand, and have opened the doors of investing to millions of people who once thought the stock market was too complicated.
At its core, an ETF is like a basket of investments; a single product that holds multiple assets such as stocks, bonds, or even cryptocurrencies. You can buy and sell it just like a regular stock on the exchange. Think of it as a shopping cart filled with small portions of different companies or assets, giving you instant diversification without the need to buy each asset individually.
Today, ETFs manage over $12 trillion in assets globally, a figure that continues to grow as investors seek more flexible and low-cost ways to grow their wealth. However, what makes 2025 especially exciting is the emergence of a new wave of crypto- and Web3-focused ETFs, such as Bitcoin ETFs, that are bridging the gap between traditional finance and decentralised markets.
This blog post will break it all down in plain English, what ETFs really are, how they work, the different types that exist, and why crypto ETFs are quickly becoming one of the hottest trends in modern investing.
By the end, you’ll not only understand the “ETF meaning,” but also why they matter in this new age of digital assets and how they’re shaping the next era of Web3 finance.
What Is an ETF?

Let’s start simple.
An ETF, or Exchange-Traded Fund, is basically a basket of investments you can buy with just one click. Instead of purchasing one company’s stock, like Apple or Tesla. You buy one ETF, and that single move gives you small pieces of many companies at once. It’s like ordering a combo meal instead of choosing every item one by one.
ETFs are built to make investing easier. They group different assets; stocks, bonds, or even crypto, and then trade on the stock market just like regular shares. You can buy them through the same app you’d use to buy a single stock.
Here’s the beauty of it: you don’t need to be an expert to start. If you believe the tech industry will grow, there’s a Technology ETF that holds a mix of top tech stocks. If you want something safer, there’s a Bond ETF that spreads your money across government or corporate bonds. The point is, there’s an ETF for almost everything now.
And it’s not just small investors who love them. Big institutions, pension funds, and even governments use ETFs because they’re low-cost, easy to manage, and transparent. Globally, ETFs now manage over $12 trillion, a number that keeps growing every year.
But here’s where it gets interesting for 2025: the world of ETFs is expanding beyond traditional markets. We now have Bitcoin ETFs and even Web3-focused ETFs that give investors exposure to the digital economy without needing to set up a crypto wallet or deal with blockchain complexities.
So, when people ask “what is an ETF?”, the real answer is this:
It’s a smarter, simpler way to invest, one that’s now opening the door to the future of crypto and decentralized finance.
How Do ETFs Work?
Now that we know what an ETF is, let’s break down how it actually works, because understanding this part helps you see why it’s such a big deal in modern investing.
Think of an ETF like a container that holds different investments. Inside that container are stocks, bonds, or even Bitcoin, depending on what kind of ETF it is. When you buy one share of the ETF, you’re basically owning a piece of everything inside that container.
Here’s an example.
Let’s say there’s an ETF that tracks the S&P 500, which is an index of the 500 biggest companies in the U.S. If Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft are all part of that index, then a share of the S&P 500 ETF automatically includes small pieces of all three. The ETF’s job is to mirror the performance of that index, if the S&P 500 goes up, the ETF usually goes up too.
That’s the beauty of it: you don’t need to pick winners or losers. You just invest in one ETF, and you’re instantly diversified.
Now, here’s where it gets interesting. ETFs trade on stock exchanges, which means you can buy or sell them at any time during the day, just like normal stocks. The price of the ETF fluctuates throughout the day based on demand and supply, and it’s typically very close to the total value of its underlying assets.
This setup provides ETFs with their greatest advantage: liquidity and flexibility. You can invest for the long term, or trade short-term, the choice is yours. It’s this flexibility that made ETFs so popular with both everyday investors and large institutions.
There’s also something called the NAV, or Net Asset Value. That’s just a fancy way of saying “the total value of all the assets the ETF owns, divided by the number of shares.” It helps investors know if the ETF is priced fairly.
Now, let’s talk about how crypto fits into this picture.
Crypto ETFs, like the Bitcoin ETFs that launched in early 2024 work in almost the same way. Instead of holding shares of companies, these funds hold or track the price of Bitcoin. So when Bitcoin goes up, the ETF’s value rises too. The big difference? You don’t have to worry about wallets, private keys, or exchanges, the ETF handles all that behind the scenes.
That’s why crypto ETFs have been called the “Trojan horse” of Web3 adoption. They quietly introduce millions of traditional investors to digital assets without requiring them to change anything about how they invest.
So, in short:
ETFs work by pooling assets, slicing them into shares, and letting you trade them easily, making investing simple, flexible, and now, with crypto ETFs, more connected to the future of finance than ever before.
Types of ETFs

ETFs come in many flavours. Some focus on traditional markets, others explore newer spaces like blockchain and crypto. But no matter what they track, the goal is the same: to make investing easier, more diversified, and more accessible.
Let’s walk through the main types of ETFs you’ll see today.
1. Stock (Equity) ETFs
These are the most common. Stock ETFs hold shares of many companies within a certain index, sector, or theme.
For example, the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) tracks the top 500 U.S. companies, Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, you name it. Buy one share of SPY, and you own a piece of all of them.
There are also sector-based ETFs, like tech ETFs that focus on innovation, healthcare ETFs that follow medical companies, or clean energy ETFs that include solar and EV firms. They give you the chance to invest in industries you believe in, without betting on a single company.
These ETFs are a favourite for both beginners and professionals because they’re easy to understand and tend to have steady growth over time.
2. Bond ETFs
Bond ETFs are for people who want stability. They invest in government, corporate, or municipal bonds. Think of them as lending your money to companies or governments, and earning small, steady returns in return.
Unlike traditional bonds, which can be hard to buy or sell quickly, bond ETFs trade easily on exchanges. So investors can get the safety of bonds but the flexibility of stocks.
During uncertain times, like recessions or crypto bear markets, many investors shift some money into bond ETFs for balance.
3. Commodity ETFs
These ETFs focus on physical assets like gold, silver, or oil. They’re often used as a hedge against inflation or market volatility.
For example, the SPDR Gold Shares (GLD) ETF lets you gain exposure to gold prices without ever needing to buy or store gold bars. Commodity ETFs are great for diversifying your portfolio beyond just stocks and bonds.
4. Index ETFs
Index ETFs follow a specific index, like the Dow Jones, NASDAQ, or S&P 500. They’re designed to match the performance of those markets, not beat them.
These are popular for passive investors, people who prefer steady, market-level returns instead of trying to “time” the market. They also tend to have very low fees, which makes them great for long-term investing.
5. Thematic and Sector ETFs
This is where things start getting creative. Thematic ETFs focus on big ideas shaping the future, like artificial intelligence, renewable energy, or the metaverse. Sector ETFs focus on specific industries, like banking, real estate, or cybersecurity.
These ETFs often attract younger investors who want their portfolios to reflect their interests or values. For example, if you believe in the growth of decentralized tech, there are even Web3 ETFs now that bundle companies building blockchain and crypto infrastructure.
6. Crypto and Bitcoin ETFs
Here’s where the Web3 connection comes alive. Crypto ETFs, like the Bitcoin ETF or the Bitwise Web3 ETF, are built to track digital assets, especially Bitcoin.
Instead of buying Bitcoin directly, investors can now buy a Bitcoin ETF through their regular brokerage accounts. The ETF either holds Bitcoin itself or tracks its price using derivatives. The result? You get exposure to Bitcoin’s performance without managing a wallet, private keys, or exchanges.
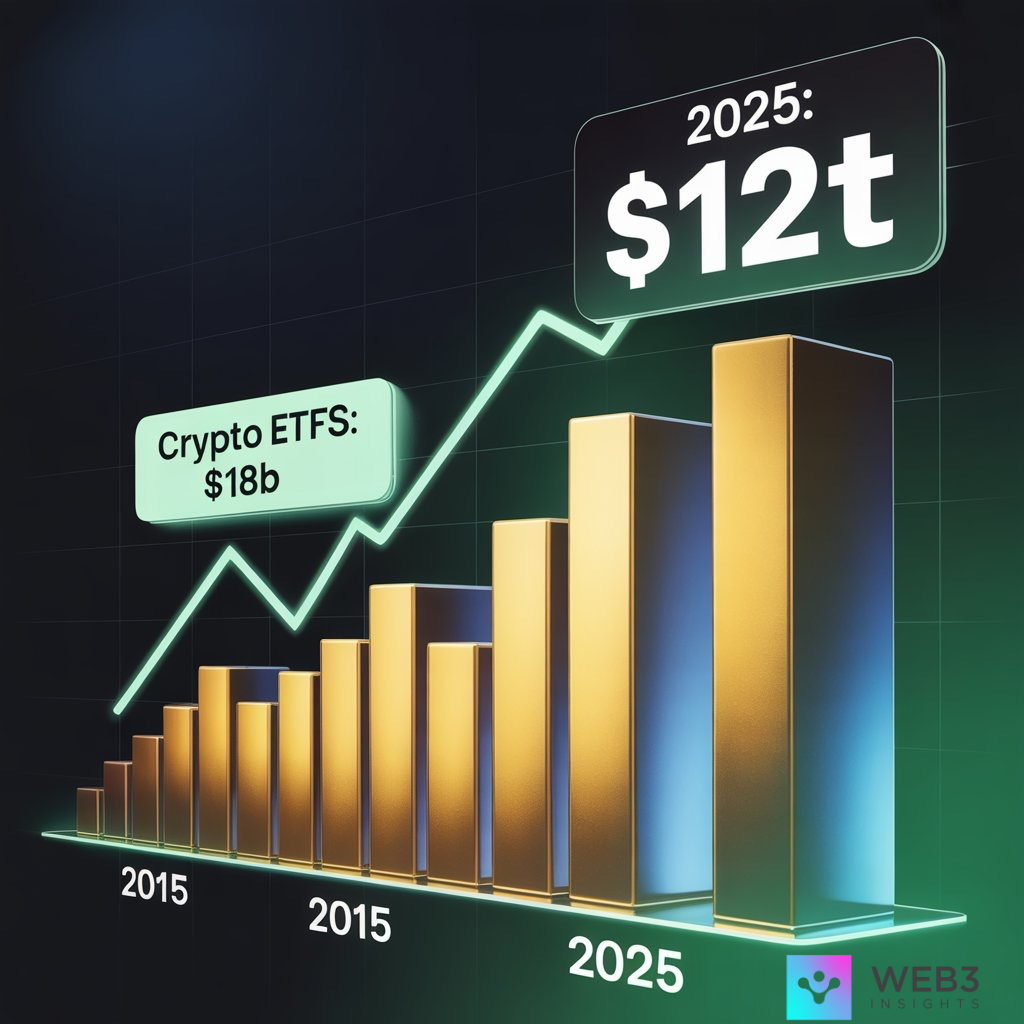
This is a massive breakthrough because it brings traditional finance (TradFi) and crypto under the same roof. In 2025, Bitcoin ETFs have already attracted over $18 billion in inflows, and more crypto ETF, including those for Ethereum, Solana, and Web3 projects, are expected to follow.
Crypto ETFs are still new, but they’re quickly becoming one of the most important tools for bridging the gap between old and new finance.
So, whether you’re into stocks, bonds, gold, or crypto, there’s an ETF that fits your vision. And the best part? You can mix and match them, creating a portfolio that’s simple, modern, and built for the Web3 era.
The Pros and Cons of ETFs

Like everything in investing, ETFs come with both good sides and a few trade-offs. Think of them as a tool, powerful when used right, but still needing a bit of understanding.
The Pros

1. Easy Diversification
With just one ETF, you can own a piece of dozens, sometimes hundreds, of assets. That means if one company’s stock drops, your overall investment doesn’t suffer too much. It’s like spreading your eggs across many baskets instead of putting them all in one.
2. Low Fees
ETFs are known for being cheaper than mutual funds. Since most ETFs just track indexes like the S&P 500, they don’t need expensive fund managers making decisions every day. This keeps the cost low, and that means more of your profit stays in your pocket.
3. Easy to Trade
You can buy or sell ETFs anytime the market is open, just like a normal stock. There’s no waiting until the end of the day like with traditional funds. It’s fast, flexible, and fits how modern investors like to trade.
4. Transparency
ETFs are required to show what they hold. So you can always check which stocks or assets you’re really invested in. That’s not always the case with other funds.
5. Access to New Markets
ETFs have opened the door to places investors couldn’t easily reach before like commodities, foreign markets, or even crypto-related assets. You can now get exposure to Bitcoin or blockchain projects without actually owning the coins.
The Cons

1. Market Risk Still Exists
Even though ETFs spread your investments, they can still lose value when the market falls. Diversification reduces risk, but it doesn’t erase it.
2. Trading Temptation
Because ETFs are so easy to buy and sell, some investors trade them too often; trying to time the market instead of holding for the long run. That can lead to losses, especially in volatile markets.
3. Tracking Error
Sometimes, an ETF doesn’t perfectly follow the index or sector it’s meant to track. This small difference, called a tracking error, can affect returns, especially over time.
4. Hidden Costs
Even though ETFs have low management fees, there are still trading costs, spreads, and taxes that can quietly eat into profits if you trade frequently.
In short, ETFs make investing simpler, cheaper, and more flexible, but they still require discipline. The trick is to use them wisely: choose the right ETF, understand what it tracks, and focus on long-term growth instead of quick flips.
Why 2025?
2025 isn’t just another year for the ETF world. It’s the year crypto ETFs truly take off.
For years, investors have sought an easy, regulated way to gain exposure to digital assets without the hassle of managing wallets, private keys, or exchange risks. Bitcoin ETFs finally made that possible. And now, in 2025, that idea is expanding into something much larger, a full movement that connects traditional finance with the cryptocurrency economy.
Since Bitcoin ETFs were approved, they have attracted over $18 billion in inflows, making them one of the most successful ETF launches in history. That kind of momentum is changing how Wall Street views digital assets. Bitcoin is no longer seen as just a speculative coin. It’s becoming a recognized asset class that sits alongside gold, bonds, and tech stocks.
But 2025 isn’t only about Bitcoin. Attention is now turning to Solana and XRP, two networks being discussed as potential candidates for their own spot ETFs. The excitement around them comes from real progress. Solana’s speed, developer activity, and growing DeFi ecosystem make it an appealing option for institutions looking for broader Web3 exposure.
At the same time, major asset managers such as BlackRock, VanEck, and ARK Invest are expanding their crypto ETF offerings. These range from Ethereum and Solana funds to full Web3 and blockchain-focused ETFs. They allow investors to support entire sectors of the crypto space without directly holding tokens, offering a safer and easier entry point for traditional money.
Global interest is also rising. Countries like Hong Kong, Australia, and several in Europe are exploring their own Bitcoin and crypto ETF approvals. This shows that the trend is not limited to the United States but is becoming a global shift toward regulated digital asset investing.
2025 marks the moment when crypto ETFs stop being an experiment and start becoming a key part of modern portfolios. From Bitcoin’s record inflows to the growing momentum around Solana and XRP funds, the ETF landscape is evolving fast, blending the worlds of Wall Street and Web3 in ways we’ve never seen before.
FAQ

What does ETF stand for?
ETF stands for Exchange-Traded Fund. It’s a type of investment fund that holds a collection of assets such as stocks, bonds, or even cryptocurrencies. Instead of buying each asset individually, you can buy one ETF and instantly own a small portion of everything inside it. ETFs trade on the stock market just like regular shares, which makes them easy to buy and sell.
What’s a crypto ETF?
A crypto ETF gives investors exposure to digital assets without needing to hold or manage the actual coins. For example, a Bitcoin ETF tracks the price of Bitcoin. When Bitcoin goes up, the ETF’s value rises too. The same goes for funds tracking Ethereum, Solana, or Web3 companies. It’s a safer and more regulated way for traditional investors to enter the crypto market without dealing with private keys or exchanges.
Are crypto ETFs safe?
Crypto ETFs are regulated financial products, which means they follow the same rules as traditional funds. They don’t remove market risk, the prices of Bitcoin and other tokens still go up and down, but they protect investors from security issues like hacks or lost wallets. The biggest advantage is that you can hold them through a regular brokerage account, just like any stock.
What makes 2025 special for ETFs?
2025 is the year crypto ETFs go mainstream. After the success of Bitcoin ETFs, new ones focused on Solana, Ethereum, and XRP are being discussed by major fund managers. With billions in inflows, global approvals, and growing institutional interest, this year represents the turning point when crypto investing becomes truly accessible to everyone.
How do ETFs make money?
ETFs make money in two main ways: through price growth and dividends. If the assets inside the ETF increase in value, your ETF shares become worth more. Some ETFs also pay dividends if the companies they invest in issue them. Investors can choose to reinvest those dividends or take them as cash.
What is the difference between an ETF and a mutual fund?
Both ETFs and mutual funds hold baskets of assets, but the main difference is how they trade. ETFs can be bought or sold anytime the market is open, while mutual funds only trade once per day after the market closes. ETFs usually have lower fees and are more transparent about what they hold.
Conclusion

ETFs have changed how people invest. They make it possible for anyone to build a diverse portfolio without needing to manage dozens of individual assets. And now, with the rise of crypto ETFs, that same simplicity is being brought into the world of digital finance.
2025 marks the moment this shift becomes impossible to ignore. Bitcoin ETFs have already proven that there’s massive demand for regulated crypto exposure. Solana, Ethereum, and XRP could be next, opening the door for investors to participate in Web3 growth through traditional channels.
The line between Wall Street and blockchain is fading. As more institutions and everyday investors join in, ETFs are becoming the bridge that connects old finance with the new digital economy.
If you’ve ever wanted to understand where crypto meets traditional investing, this is the time to pay attention. The next generation of ETFs is not just about stocks and bonds, it’s about building a new kind of financial future, one block at a time.
Subscribe to Web3 Insights to stay updated on the latest ETF trends, crypto market shifts, and the technologies reshaping global finance.