Think of personal data as the fuel powering our digital world. As this data becomes more valuable, people worry about their privacy and who can access their information. Many fear that the internet might lose its freedom and openness.
Why? Because big companies are collecting tons of data, and there’s a lot of online tracking happening. Entering Web3, it’s a game-changer!
Web3’s decentralized tech can give you more control over your own data. In this article, we’ll break down Web3 & data privacy in simple terms. By the end, you’ll know how to better protect your information in this new digital landscape.
Understanding Data Privacy: Traditional vs. Web3
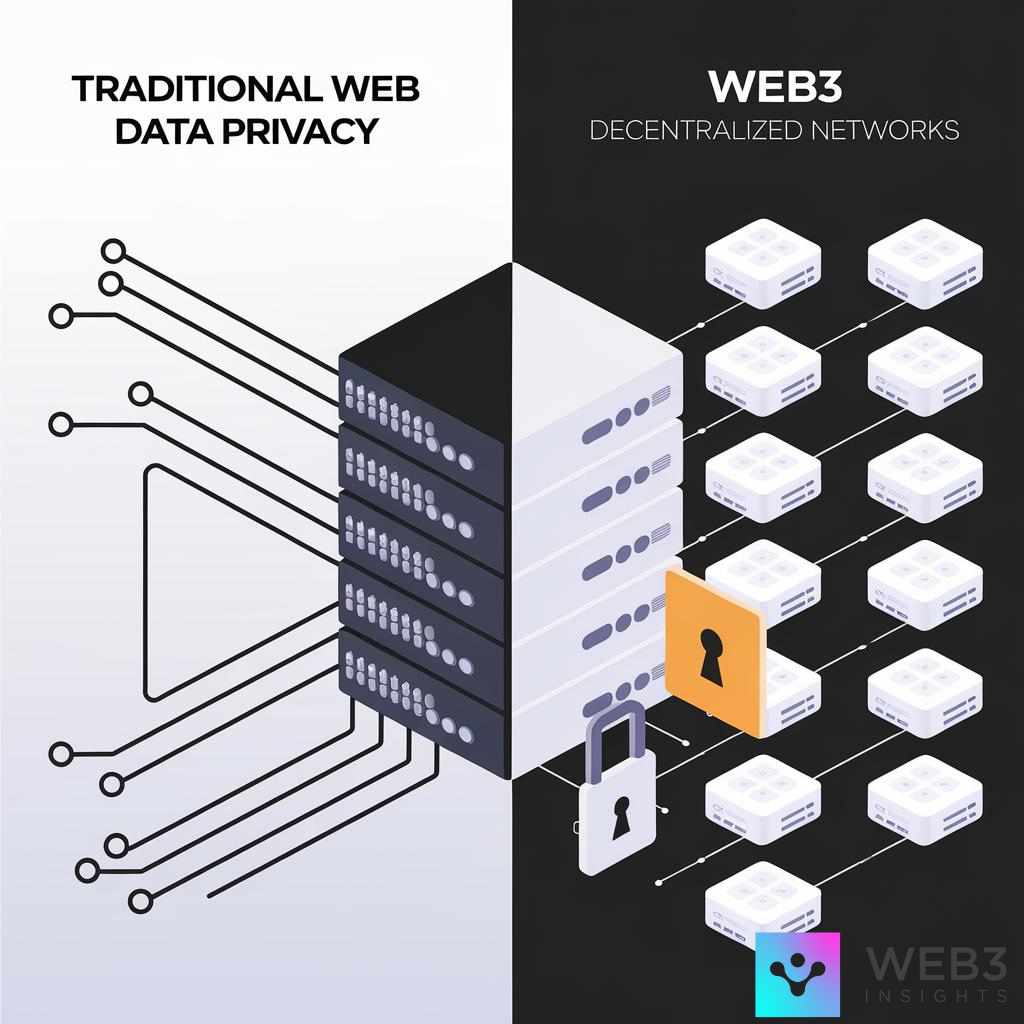
Traditional Data Privacy
In the traditional Web 2.0 context, data privacy primarily focuses on protecting personal information from unauthorized access, misuse, or breaches. It revolves around ensuring that companies and organizations that collect and store data follow regulations and standards to keep it secure.
Users often have limited control over their data, with large corporations serving as the custodians of this information. These companies decide how data is collected, used, and shared, and users generally have to trust them to manage their information responsibly.
Data Privacy in Web3
In the context of Web3, data privacy takes on a much broader and more significant role. It isn’t just about protecting data from being misused or accessed without permission; it’s about giving individuals full control over their personal information throughout its entire lifecycle. This includes:
- Collection: Users have the power to decide what data is collected and who collects it.
- Storage: Individuals can choose where and how their data is stored, often using decentralized systems.
- Processing: Users can control how their data is processed, ensuring that it’s only used in ways they approve.
- Sharing: People can decide with whom and under what conditions their data is shared.
- Deletion: Users have the right to fully delete their data, removing it from all systems if they wish.
In summary, while traditional data privacy is about protection, Web 3 data privacy is about control and ownership.
Key Aspects of Data Privacy in Web 3

1. Ownership: In Web3, your data is your property. You are not just a passive subject in data collection; instead, you own your digital footprint. This extends to all kinds of personal data, from basic details like your name and email to complex data generated through your online activities.
2. User Control: Web3 gives you unprecedented control over your data. You can decide exactly what information to share, with whom, for what purpose, and for how long. This means you can grant or revoke access to specific pieces of your data, even down to individual details.
3. Transparency and Auditability: A core principle of Web3 is complete transparency in how companies handle data. You can see exactly how they use your data, who accesses it, and why. Blockchain technology supports this by providing an unchangeable record of all data transactions, so you can track the entire history of your data.
4. Decentralized Storage: Unlike the centralized servers used in Web 2.0, Web3 uses decentralized storage solutions. You can store your data across a network of distributed systems or in personal data stores that you control. This reduces the risk of massive data breaches and unauthorized access.
5. Cryptographic Security: Web3 uses advanced cryptographic methods to protect your data. This includes end-to-end encryption, which secures your data both as it moves across the internet and while it is stored. Additionally, techniques like zero-knowledge proofs allow for verifying data without actually revealing the data itself.
Challenges & Solutions in Web3 & Data Privacy

Web3, the next generation of the internet, offers exciting possibilities like decentralization, greater transparency, and user control. However, it also brings some challenges, especially around data privacy.
Here’s a look at a few main issues:
1. Scalability Issues
The Challenge:
Web3 relies on blockchain technology, which is secure but can struggle with handling a large number of transactions at once. When too many people use the network, it can slow down and become expensive to use.
The Solution:
To solve these problems, developers are working on new technologies like layer-2 scaling (which processes some transactions off the main blockchain), sharding (which splits the blockchain into smaller pieces), and new methods for validating transactions. Developers are still creating these solutions, so it’s important to keep testing and improving them to ensure they scale without compromising privacy or security.
2. User Experience and Adoption Hurdles
The Challenge:
Web3 can be complicated for new users. Managing private keys, understanding decentralized apps (dApps), and dealing with unfamiliar technology can be intimidating. This complexity makes it hard for many people to start using Web3, which slows down its adoption.
The Solution:
Making Web3 easier to use is key to getting more people on board. This includes creating simpler interfaces, improving the security of wallets, and offering better education on how Web3 works. Integrating Web3 with existing systems that people already know can also help ease the transition and encourage more people to try it out.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Concerns
The Challenge:
Web3 operates in a space that’s mostly unregulated, which raises questions about how it fits with existing data privacy laws, like the GDPR in Europe. Since Web3 is all about decentralization, it’s hard to determine who is responsible for correctly handling data.
The Solution:
To stay compliant with privacy laws, Web3 platforms need to build privacy features into their systems from the start. This could involve encrypting data, giving users more control over their information, and making sure the platform can comply with regulations while staying true to the decentralized nature of Web3.
Conclusion
Web3 is changing the way we think about the internet by putting data privacy at its centre. Unlike today’s Web2, which often puts control in the hands of big companies, Web3 aims to give users more power over their data. This shift could address many privacy concerns we face today.
However, getting to a fully functional Web3 comes with challenges. We need to resolve issues like scalability (how well it handles growth), user experience, regulatory compliance, interoperability (how well different systems work together), and security.
To make Web3 successful, we need collaboration among developers, regulators, and users. The goal is to create a Web3 that is innovative, secure, inclusive, and meets privacy standards. By tackling these challenges, Web3 can deliver on its promise of a more decentralized internet that enhances user control, protects privacy, and promotes a fairer digital world.