As blockchain technology grows, different networks often operate in isolation, making working together hard. Cross-chain interoperability aims to solve this problem by allowing different blockchains to communicate and share data smoothly. By bridging the gaps between networks, cross-chain interoperability is a key step toward a more connected and powerful blockchain future.
This article will uncover everything you need to know about cross-chain interoperability. Sit tight!
What Is Cross-Chain Interoperability?
Cross-chain interoperability allows different blockchains to share information and transfer value, making decentralised applications (dApps) more functional and enabling collaboration across networks. Today, many blockchains work in isolation, much like the early days of the internet, which limits their ability to share resources and data.
Interoperability solves this problem by connecting these blockchains, improving their efficiency and scalability. This opens up new possibilities for innovation in finance, supply chain management, and digital identity.
Why Is Cross-Chain Interoperability Important?
Interoperability in blockchain technology makes it possible for different blockchains to share assets and data. Normally, when two parties use the same blockchain, like Bitcoin, exchanging information and value is easy. But this process becomes difficult when different blockchains are involved.
Interoperability aims to solve these issues, making it easier for parties to transact across different blockchains. Cross-chain interoperability is more than just a technical achievement; it’s essential for the future growth and adoption of blockchain technologies.
Interoperability also tackles one of the blockchain industry’s major challenges: isolated networks, or “silos.” By enabling seamless exchanges of value and data across different blockchains, interoperability increases liquidity, enhances security through shared information, and opens up new markets and business models that were previously impossible.
Key benefits of cross-chain interoperability include:
- Improved Scalability and Efficiency: Blockchains can share workloads, reducing congestion and making the system more scalable and efficient.
- Enhanced Liquidity and Access to Assets: Interoperability allows assets to move freely across networks, increasing liquidity and enabling easy trading across different platforms.
- Greater Innovation and Collaboration: By breaking down barriers between blockchains, interoperability fosters a collaborative environment where developers can create versatile dApps, driving technological progress.
- Seamless User Experience: For users, interoperability simplifies interactions with blockchains, allowing them to use a single interface to access different networks, making blockchain technology more accessible and easier to use.
How Cross-Chain Interoperability Work
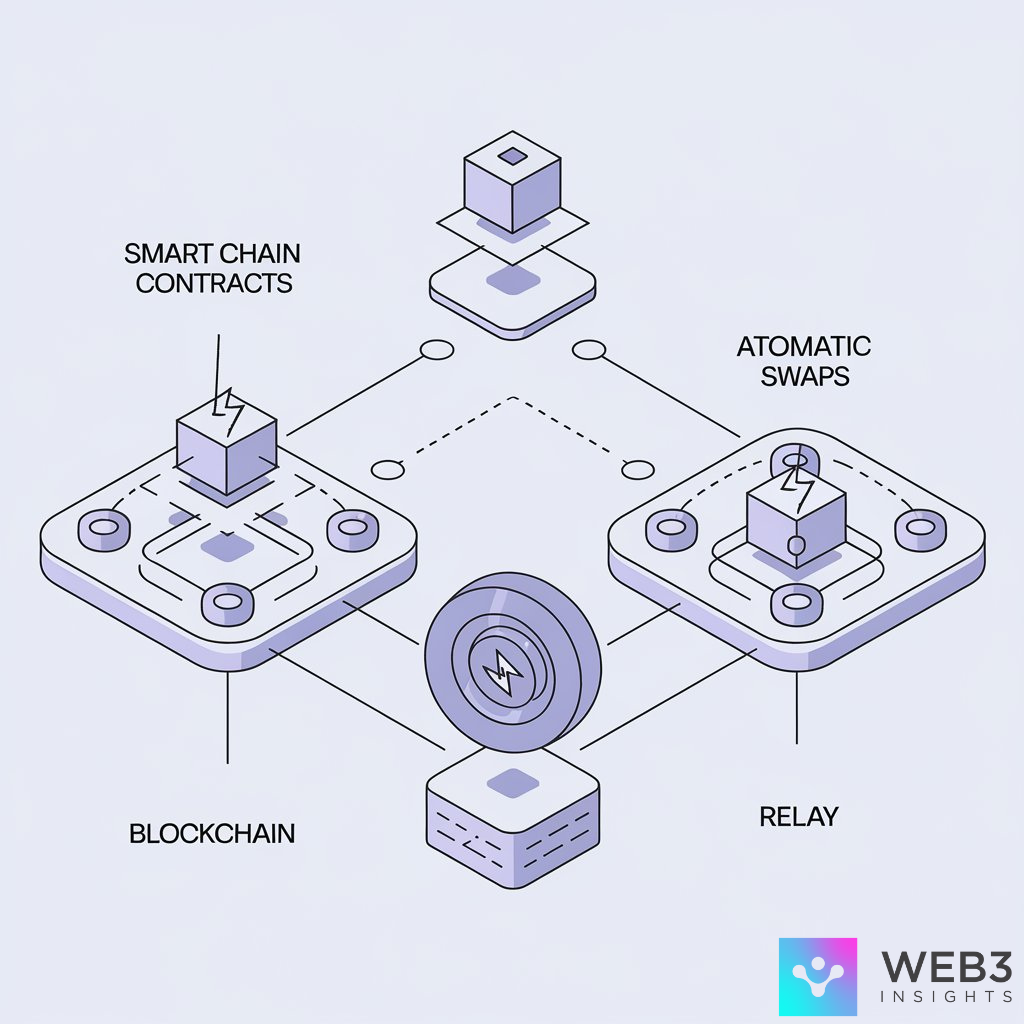
Let’s delve into the various solutions that are breaking down these barriers. Some of the enabling technologies are:
Atomic Swaps:
Atomic swaps enable peer-to-peer exchanges of cryptocurrencies between different blockchains without relying on a third party. They utilize smart contracts to ensure that both parties either receive the agreed assets or the transaction is void, enabling trustless trading.
Relays:
Relays help one blockchain keep track of what’s happening on another. They act like bridges, enabling data sharing and transaction checks between different blockchains.
Light Clients & Oracles:
Light clients and oracles work together to make cross-chain communication possible. The Light clients are small programs that run on another blockchain and interact with the main one. Oracles fetch data from the source blockchain and send it to the target blockchain, allowing it to verify information without needing to process the entire blockchain history.
Mechanisms of Cross-Chain Interoperability

1. Cross-Chain Bridges
Cross-chain bridges are tools that link different blockchains, making it easier to transfer assets and data securely. These bridges typically lock an asset on the original blockchain and create a matching token on the destination blockchain. When you want to move back, the bridge destroys the token on the destination blockchain and unlocks the original asset.
2. Shared Validators
Shared validator protocols use the same set of validators to secure transactions on multiple blockchains. These validators check transactions on both chains, ensuring that data can be exchanged securely without relying on trust.
3. Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 solutions are built on top of a main blockchain, making transactions faster while still being secure. Some Layer 2 solutions, like rollups, are now adding features to allow assets and data to move between Layer 2 networks and the main blockchain, or even between different Layer 2 networks.
4. LayerZero
This protocol enables lightweight message passing between blockchains, allowing for secure and reliable communication. LayerZero uses ultra-light nodes that interact with oracles and relayers to facilitate cross-chain transactions efficiently.
Role of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are like digital agreements written in code that automatically execute when conditions are met. They’re essential in cross-chain transactions because they automate the process and ensure both parties are protected.
For example, in atomic swaps, smart contracts make sure that if one party doesn’t deliver, the transaction is automatically cancelled.
Limitations, Challenges and Risks of Blockchain Interoperability
While blockchain interoperability connects different blockchain networks and opens up many opportunities, it also brings several challenges related to technology, security, scalability, governance, and dependency. To overcome these challenges, the blockchain community must work together to create solutions that are secure, scalable, standardized, and able to function in a decentralized way.
Limitations
- Blockchain Differences: Blockchains are very different from each other, much like how different species vary in nature. These differences in design, how they reach agreement (consensus), and security make it difficult for them to work together smoothly.
- Scalability Issues: Current interoperability solutions can add extra processing work, which may slow down the entire blockchain system.
Challenges
- Security Risks: Connecting blockchains can create new opportunities for hackers. If there are security flaws in any part of the system, like bridges or oracles, it could cause widespread problems. Strong security is crucial to keep cross-chain transactions safe and reliable.
- Lack of Standards: There aren’t widely accepted standards for how blockchains should communicate with each other, which leads to a fragmented system. With many different protocols, it’s hard to make everything work together.
- User Experience Difficulties: Many current interoperability solutions are complicated for users. They often require users to navigate complex interfaces and manage multiple wallets across different blockchains.
Risks
- Centralization Problems: Many interoperability solutions rely on centralized entities, like bridge operators or oracles, which can become single points of failure. This reliance can go against the decentralized nature of blockchain technology.
- Data Accuracy Concerns: Ensuring that data shared between blockchains is accurate and trustworthy is essential. If the data is incorrect or manipulated, it could disrupt applications and cause financial losses. Protecting the integrity of cross-chain data is critical for safe and reliable blockchain interactions.
The Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
The Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is an open standard that allows different blockchains to communicate with each other. It helps move tokens and messages across various blockchains, no matter what technology they use.
CCIP meets the growing need for more advanced cross-chain interactions by offering a simple interface connecting different blockchains. It also integrates well with other services, simplifying the process of building complex cross-chain applications and operations.
The Future of Cross-Chain Interoperability
The future of cross-chain interoperability is bright, with advancements that promise to make blockchain networks more connected and efficient. As technology improves, we can expect to see the development of universal standards and protocols. These will make it easier and safer for different blockchains to work together, allowing assets and data to move smoothly between networks.
This progress could also drive more widespread use of blockchain technology. When businesses and individuals can easily access and use resources across multiple blockchains, it lowers the barriers to entry. This will encourage more innovation and lead to new decentralized applications (dApps) that use cross-chain features. Industries like finance, supply chain, and gaming could see exciting new possibilities as a result.
However, we need to address some challenges for this future to become a reality. Security concerns and governance issues are critical, and stakeholders must work together to find solutions ensuring safe and reliable cross-chain interactions.
In summary, cross-chain interoperability has the potential to transform the blockchain world by making it more connected and accessible. As this technology continues to develop, it will play a key role in the growth and adoption of blockchain networks.